It's no news that fintech has transformed financial services as we know them. As a fintech start-up, you're probably wondering how to stand out in an industry so focused on innovation.
Competition is fierce and relying on technology as the unique selling point is not enough. To succeed, you need a business model that can drive growth and a way to make a difference.
Gassmann and his team, authors of the Business Model Navigator methodology and the book with the same name, analyzed 55 business model patterns. They concluded that 90% of business model innovation is based on a recombination of existing ideas, strategies, and models. With this in mind, let's take a look at what fintech companies are doing today to drive change and make a profit, so you can start building your own recipe.
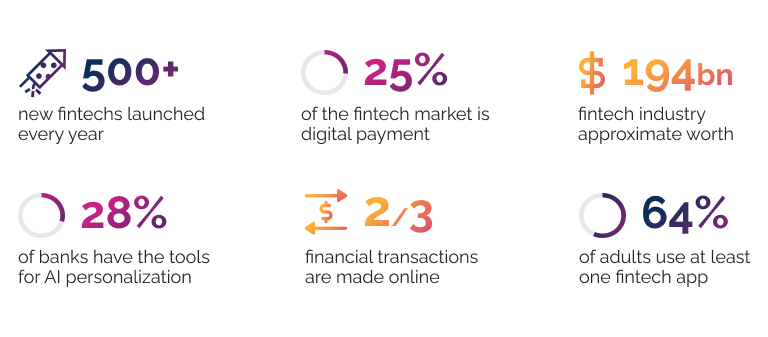
Sources: ATOS, McKinsey, EY, EMR
Understanding fintech business models
Simply put, a business model represents the underlying logic of your business. It's the way you create value for other people or companies and make money as a result. Here is how some of the most popular fintech business models operate based on these two aspects.
How fintechs create value
Model 1. Alternative financing and insurance
One way fintech companies create value is by providing convenient alternatives to those offered by traditional lenders or insurance companies.
Peer-to-peer lending, crowdfunding, and crowdsourcing fintechs open up new opportunities to secure funding. Similarly, alternative credit scoring helps individuals who would otherwise have difficulties receiving financing from a traditional lender.
Especially in the gig economy, where the focus on entrepreneurship and self-employment is on the rise, alternative credit scoring provides more accessible options. Fintechs use advanced algorithms to assess the creditworthiness of individuals and small businesses in a more flexible manner.
A similar fintech trend is visible in InsurTech. By using algorithms and additional sources like health data from connected devices (IoT), fintech companies can tailor insurance based on the customer's lifestyle and medical history. While insurance companies only look at a small portion of demographic information, InsurTech uses a wealth of alternative data to cover customers that fall outside the boundaries of conventional insurance underwriting.
Model 2: Secure payments and transfers
Fintechs that offer secure and convenient alternatives to traditional payment methods are another popular business model. These platforms facilitate online payments, money transfers, and digital wallet services, with well-known examples including PayPal, Stripe, Apple Pay, and Google Pay.
For a long time, costly and time-consuming integrations have been the industry norm. Online merchants had to integrate and configure each payment method individually. The rise of all-in-one, pre-configured payment solutions is gradually changing the game. This model enables fintech companies to offer a variety of payment methods, from credit and debit cards to digital wallets, through a single integration.
Model 3: Do-it-yourself financial solutions
Fintech companies empower users to pay, invest, and manage finances on their own, with the least amount of external intervention. Robo-advisors and personal finance management (PFM) are two examples of business models that cater to this do-it-yourself approach. Robo-advisors are generally cheaper than actual financial advisors and provide individuals with data-driven insights to manage and expand their investment portfolios.
Similarly, personal finance apps provide users with more control over their budget. Apps like Mint, YNAB, or Cash App give users an easy way to track their spending, manage their savings, and look over their investments. This helps them get a clearer picture of their cash flow and, as a result, develop better financial habits.
Model 4: Digital banking services
By doing away with the operational costs involved in running a brick-and-mortar bank, neobanks and digital banking providers offer significantly lower fees.
Coupled with the convenience of virtual bank accounts, digital payments, and quicker response times, digital banking provides another successful business model employed by companies like Chime and Monzo. Established less than two decades ago, these companies have already managed to attract a big portion of users from traditional banks.
Model 5: API and infrastructure providers
Plaid, Galileo, and Marqueta are all good examples of companies offering APIs and infrastructure services that enable other fintechs to build and scale their solutions. APIs allow financial applications to share data between them and enrich their scope.
This model involves aggregating important financial data from multiple sources and then charging business customers a fee for connecting to the API and accessing this shared data.
How fintechs make money
Fintech companies use different approaches to monetize their products and services. While there are hundreds of ways fintechs make money, below are some of the most popular ones.
1. Subscription revenue model
Companies using this model charge a recurring monthly or yearly fee in order for customers to use their product. While subscriptions are a common revenue driver for SaaS in general, it seems that we are only beginning to see their impact in the fintech industry.
The introduction of subscription models in consumer banking and insurance is an ongoing process. “Challenger banks” such as Monzo, Revolut, Sterling, and Klarna are some of the first to implement a subscription-based model.
In terms of fintech products, subscription fees are prevalent with personal finance apps, robo-advisors, and investment apps. Subscriptions have steadily grown as the preferred method over the past decade, with analysts assuming that 75% of products will be available under a subscription model as early as 2023.
2. Transaction revenue model
Based on their profile, there are various types of transactions fintech companies can monetize.
For example, peer-to-peer money transfer apps like Venmo or PayPal charge a small percentage fee for users who want instant transfers from the app to their bank account.
Credit card processing fees also allow payment processors like Stripe or Square to earn a percentage of the transaction.
Fintech companies have found different ways to build a business around these fees, often at a lower price than regular financial institutions.
3. Freemium revenue model
In a “freemium” pricing model, some features are included for free, but users need to pay to unlock advanced features. The main idea behind this model is that once users like the basic version, they are more likely to purchase the premium options.
Neobaks are increasingly adopting the freemium model as a way to get their foot through the door and earn the trust of new users. Initially launched as a money transfer app,
Revolut has come a long way becoming a key player in the challenger bank market. One of their strategies was to keep basic services free of charge and introduce premium service tiers at a later date.
4. Referral revenue model
Fintechs sometimes partner with other companies to promote third-party services and products. As a result, they earn a referral fee each time these products or services are sold.
Similar to the freemium model, these companies usually don't charge anything for their core offer, but they present users with premium financial products like personal loans and credit cards. Each time a user of their free product signs up for a personal loan or credit card, the fintech company earns money from their partners.
Factors to consider when building your fintech business model
The business model you choose sets your course for the future, from the customers you target to the way you communicate and market yourself as a fintech.
Starting from the early stages it's important to look at:
-
Your value proposition i.e. what sets you apart from other fintech companies
-
Your customer segments and their potential unmet needs and expectations
-
Your revenue model and how you plan to monetize your fintech product or service
-
The infrastructure and technology stack that power and secure your fintech solution
-
Your distribution channels i.e. how you deliver your fintech product or service to your customers
-
The partnerships you create with other companies and financial institutions
All of these elements work together as parts of the same mechanism that generates profit for your fintech and delivers value to your customers.
Defining your fintech business model innovation matrix
Investing time in defining and refining your fintech business model is well worth it. Business model innovation is typically the most lasting form of innovation and one of the best ways to differentiate yourself.
There are different tools you can use for this, including the Business Model Innovation Matrix. This is a simple 2x2 matrix you can leverage to evaluate and compare fintech business models and identify potential areas of improvement that could give you a competitive edge.

Source: https://appfluence.com/productivity/business-model-innovation-matrix/
Innovation quadrant
The top-left quadrant of the matrix evaluates the level of innovation of a given business model. It looks at whether the model introduces new technologies, new services, new processes, or all of them in the case of truly disruptive solutions.
For example, one of the ways fintech companies gained an advantage over traditional financial institutions is through unbundling.
Conventionally, financial services have been bundled under one roof, with banks offering investment opportunities, insurance, loans, and credit cards. With the fintech boom, highly specialized competitors appeared, who took apart these bundles and started focusing on a few select services.
This new way of doing things coupled with new processes and technologies like AI or blockchain, allowed fintech companies to take over significant portions of business from banks and focus on delivering value more effectively.
Efficiency quadrant
The top-right quadrant of the matrix focuses on the efficiency of the business model and how it uses existing resources to reduce cost. Fintech businesses like digital banking providers and neobanks employ a fully digital infrastructure to reduce operational costs and, as a result, cut down fees and expenses for their customers.
By eliminating the need for physical branches, fintechs can provide more competitive pricing and better interest rates.
At their core, fintechs use technology to enhance financial services and products. However, the same technologies can be leveraged to automate internal operations and make better decisions.
For example, many fintech businesses use machine learning algorithms and consumer data to assess market sentiment and adjust their strategy accordingly. Data analytics helps them develop tailored marketing strategies, enhance customer acquisition and retention, and identify emerging trends.
Stability quadrant
The bottom-left quadrant of the matrix looks at the stability of a given business model. One of the main challenges fintech start-ups face is balancing the desire to disrupt with the need to grow sustainably and provide long-term value.
There are several key risk factors fintech start-ups need to take into account to secure their stability.
-
Short-term thinking and investor pressure to grow quickly and provide high returns can lead to economic volatility.
-
When fintech companies overrun their operational capacity and fail to standardize procedures they are susceptible to mistakes, including service failures and security breaches. This leaves them vulnerable to cyberattacks and fraud - money laundering, identity theft, credit scams, etc.
-
If regulatory requirements are not met this can result in destabilizing fines and further damage to the company's market reputation. To keep up with the rate of technical progress, regulatory standards tend to change quite fast, making it even more challenging to stay compliant.
Growth quadrant
The bottom-right quadrant evaluates the potential for growth of the business model by using new markets to increase revenue.
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) have been consistently overlooked by banks who don't tailor their products to match business life stages or simply find the cost of serving SMEs disproportionate to the gains.
However, fintech companies are beginning to step in, with solutions that solve SME problems gaining more traction. Banking for freelancers or bookkeeping for micro-businesses are just two of the ways fintechs gain new ground.
Demographic-focused products are another market opportunity fintechs have been capitalizing on. Platforms like EverSafe help the elderly protect their savings against financial fraud and identity theft.
Camino Financial provides funding through peer-to-peer lending to minority-owned ventures.
Niche fintech has been opening up new territories where companies can expand their footprint and gain a competitive advantage.
Niche fintech opportunities for your business
As customers are getting personalized experiences in other areas of their lives, such as entertainment or social media, financial services and products need to keep up.
Fintechs have been using this hyper-personalization approach to tackle issues faced by niche communities and businesses and to expand into new markets. According to industry statistics, 18% of investment last year went into personalized financial management alone. This number likely grows when considering other highly specialized fintechs.
Fintech start-ups are able to innovate at a pace and scale that isn't accessible to larger institutions still focused on one-size-fits-all solutions.
As a founder, investor, or a fintech software development company, these are exciting times. Fintechs operating in niche markets don't only face less competition, but they also enjoy a higher level of loyalty from customers and more room for growth.
Here are some promising fintech niches to look into.
Financial inclusion
Financial technology allows underserved populations, minorities, and small businesses access to more inclusive banking and lending services. In this niche, the great differentiator is not the financial product or service itself, but how this product or service is offered and for whom.
The target audience can range from minority groups such as people with disabilities to overlooked demographic segments like teenagers or the elderly.
Sustainable finance and green fintech
As consumers and investors increasingly prioritize sustainability, fintechs that focus on ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) criteria are gaining traction.
From platforms that calculate and track carbon offset to green payment solutions, this niche is likely to see increasing investments with regulatory bodies worldwide encouraging sustainable finance practices.
RegTech and industry-focused fintech
Niche fintechs cater to a variety of industries, from education and non-profit to transportation and other financial institutions as well.
One such example is Regtech, where fintech companies help financial actors navigate complex regulations and stay compliant with industry requirements. Financial services are among the most heavily regulated sectors, making RegTech a fast-growing model.
Personal financial management
Millennials are known to dislike traditional financial institutions. They are also the generation that will inherit the largest amount of personal wealth. Money management is of growing concern for this segment, opening up an opportunity for fintechs to provide personalized services for how individuals budget, invest, and manage their money.
Personal financial wellness is a core concern for upcoming generations, so fintech products that encourage financial education and provide better control over finances are likely to thrive.
Conclusion
The fintech industry has seen a huge uptake in start-ups trying to find their place and make their mark. This has raised concerns about a potentially oversaturated market.
However, as fintechs are refining their approach it has become obvious that this is not the case. Entire customer segments and business sectors have needs and demands that are just beginning to be met.
By understanding the various niches within the industry and developing a robust business model, you can position your Fintech venture for success.